
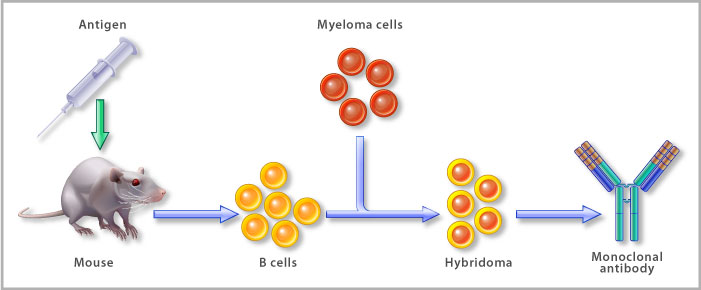
The technique consists of extracting effector B cells from the spleen of previously immunized animals.
#ANTIBODY PRODUCTION PROCESS HOW TO#
These two researchers discovered how to create a stable hybrid cell line able to secrete a high amount of antibodies specific to a unique epitope of an antigen, commonly known as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Hybridoma technology was first developed by Milstein and Köhler in 1975.
You can also take our online quiz to help you decide the best solution according to the timeframe and funding of your project. In this article, we describe the main antibody production processes, as well as their advantages and disadvantages, to help you choose the one that best matches your unique requirements. However, being a technically demanding process, the production of antibodies requires an in-depth knowledge of the available processes to choose the best one for each project and application. Unlike expensive chromatographical and analytical techniques, the development of antibodies for monitoring purposes possesses the advantage of fast detection and sensitivity, while at the same time allowing the visualization and quantification of specific markers in environmental and clinical samples. Antibodies are recurrently used for biomedical research (ELISA, Western Blot, Immunohistochemistry, Immunofluorescence Microscopy, Immunoprecipitation, among others) and as highly sensitive biosensors for food safety and environmental monitoring applications. Antibodies are highly sensitive and specific biomolecules, with the ability to detect low quantities of antigens in samples including drugs, toxins, small proteins, virus, and even pathogens.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
